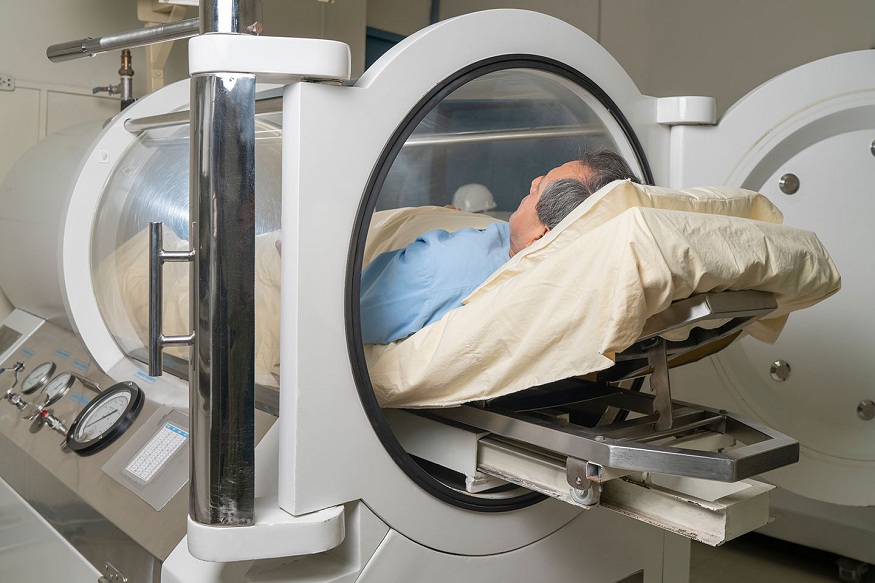
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a scientifically supported medical treatment that enhances the body’s ability to heal by delivering 100% pure oxygen under increased atmospheric pressure. When you breathe oxygen inside a hyperbaric chamber, your lungs absorb much more oxygen than they can under normal conditions. This high concentration of oxygen dissolves directly into your bloodstream, increasing the amount available to tissues and organs that need it most. The result is improved healing, faster recovery, and a reduction in inflammation.
The Science of Oxygen and Cellular Repair
Oxygen is essential for energy production and cellular repair. When tissues are damaged — due to injury, surgery, or chronic disease — their oxygen supply is often limited. This oxygen shortage slows healing and increases the risk of infection. By elevating oxygen pressure, HBOT enhances tissue oxygenation to levels far above what can be achieved by breathing oxygen at normal atmospheric pressure.
This increased oxygen availability helps cells perform crucial repair functions. It stimulates the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule responsible for cellular energy. It also accelerates the formation of collagen, a vital protein in wound healing, and improves the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). HBOT effectively “supercharges” the body’s natural repair systems.
Cellular and Molecular Effects of HBOT
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy triggers several beneficial physiological effects that promote healing:
Enhanced Collagen Production
Collagen is the structural framework for skin, tendons, and connective tissue. Oxygen is necessary for the hydroxylation of proline and lysine — two amino acids crucial for the stability of collagen fibers. By increasing tissue oxygen levels, HBOT accelerates collagen synthesis, leading to stronger wound closure and reduced scar formation.
Improved Blood Flow and Angiogenesis
HBOT stimulates the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other signaling molecules that promote the growth of new capillaries. These newly formed vessels restore oxygen flow to previously hypoxic or damaged tissues, ensuring long-term improvement in tissue health and repair.
Enhanced Immune Function
White blood cells, especially neutrophils and macrophages, require oxygen to destroy bacteria and clear away dead tissue. HBOT increases the oxygen concentration in plasma, allowing immune cells to reach and disinfect even poorly perfused regions. This makes it particularly valuable for treating infections in wounds that do not heal with standard therapy.
Reduced Inflammation and Swelling
Hyperbaric oxygen reduces inflammation by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting antioxidant enzyme activity. The pressurized environment also induces vasoconstriction — narrowing of blood vessels — which reduces swelling without compromising oxygen delivery. This mechanism is beneficial for trauma recovery, sports injuries, and post-surgical healing.
Clinical Applications
HBOT has a wide range of medical applications. It’s commonly used to treat diabetic foot ulcers, radiation tissue damage, carbon monoxide poisoning, and non-healing surgical wounds. It has also been applied in the recovery process for traumatic brain injury and ischemic stroke, where improved oxygenation supports brain cell regeneration.
In diabetic ulcers, for example, HBOT helps by increasing oxygen delivery to ischemic tissue and stimulating the growth of new capillaries. Studies have shown that patients receiving HBOT experience a significantly higher rate of wound closure compared to standard care alone.