Key Take a ways:
- Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a rare vascular disorder affecting the blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord.
- AVM is characterized by abnormal tangles of blood vessels that bypass the capillary system, disrupting normal blood flow and causing health issues.
- The exact cause of AVM is unknown, but it is believed to be a congenital condition that develops during fetal development.
- Symptoms of AVM can vary but may include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in limbs, difficulty speaking, vision problems, and balance issues.
- Diagnostic tools for AVM include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT) scans, Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA), and Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Ultrasound.
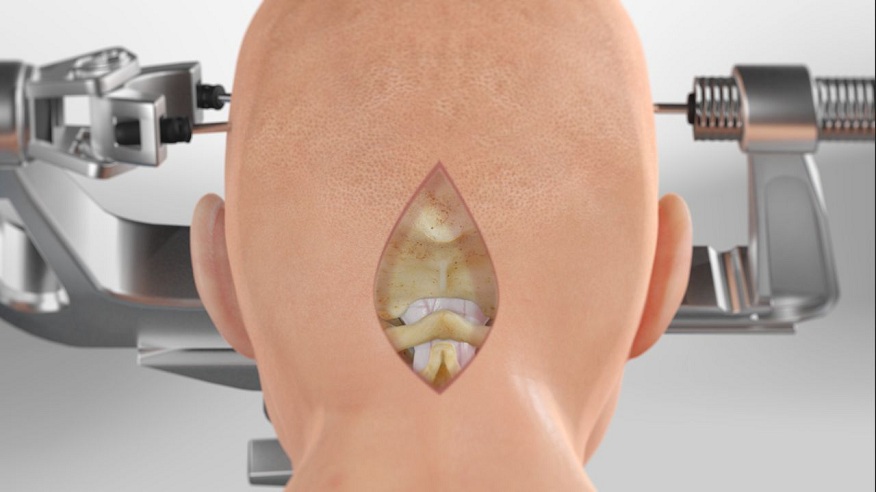
- Advancements in surgical techniques, such as intraoperative angiography, have improved the success rates of AVM treatment.
- Non-invasive treatment options for AVM include radiosurgery using focused radiation to shrink the malformation.
- Recovery and rehabilitation after AVM surgery may involve post-operative care instructions, physical and occupational therapy, as well as psychological support.
Understanding Arteriovenous Malformation: Causes and Symptoms
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a rare vascular disorder that affects the blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when there is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins. This condition is often present at birth and develops as the individual grows.
What is Arteriovenous Malformation?
Arteriovenous Malformation is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain or spinal cord. Unlike normal blood vessels, which form a network of arteries that branch out into capillaries and then join together to form veins, AVMs have direct connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This disrupts the normal blood flow and can lead to serious health issues.
Causes of Arteriovenous Malformation
The exact cause of Arteriovenous Malformation is still not fully understood. It is believed to be a congenital condition, meaning it develops during fetal development. Genetic factors may also play a role in the development of AVM. However, in most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Recognizing Symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation
The symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation can vary depending on the location and size of the malformation. Some common symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness in the limbs
- Difficulty speaking or understanding language
- Vision problems
- Balance and coordination issues
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques for Arteriovenous Malformation
Diagnosing Arteriovenous Malformation requires a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced imaging techniques. Over the years, there have been significant advancements in diagnostic tools and techniques for AVM.
Advancements in Arteriovenous Malformation Diagnosis
Advancements in medical imaging technology have revolutionized the diagnosis of Arteriovenous Malformation. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans are commonly used to visualize the blood vessels and identify the presence of AVM. These imaging techniques provide detailed images that help in planning the appropriate treatment approach.
Key Imaging Techniques for Identifying Arteriovenous Malformation
There are several key imaging techniques used to identify Arteriovenous Malformation:
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): This technique uses a combination of magnetic resonance imaging and intravenous contrast agents to visualize the blood vessels.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): DSA is a highly specialized X-ray technique that allows detailed visualization of the blood vessels to identify AVM.
- Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Ultrasound: TCD is a non-invasive technique that uses ultrasound waves to evaluate the blood flow in the brain.
Pioneering Diagnostic Tools in Arteriovenous Malformation Research
Researchers are constantly exploring new diagnostic tools to improve the detection and understanding of Arteriovenous Malformation. One such tool is functional MRI, which provides information about the brain’s functioning along with the structural images. This helps in assessing the impact of AVM on brain activity.
Exploring Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformation
The treatment approach for Arteriovenous Malformation depends on several factors such as the size, location, and symptoms associated with the malformation. There are both invasive and non-invasive treatment options available.
Invasive vs. Non-invasive Treatment Approaches
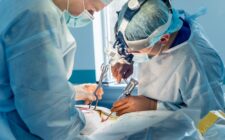
Invasive treatment approaches involve surgical interventions to remove or occlude the AVM. These procedures include microsurgical resection and endovascular embolization, which aim to eliminate or reduce the blood flow through the AVM. Non-invasive treatment options include radiosurgery, which uses focused radiation to target and shrink the AVM.
Novel Surgical Techniques for Successful AVM Treatment
Advancements in surgical techniques have greatly improved the success rates and outcomes of AVM treatment. One such technique is the intraoperative angiography, which allows real-time imaging during the surgery to confirm the complete removal or occlusion of the AVM.
Emerging Therapies in the Treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation
Researchers are constantly exploring new therapies for the treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation. One promising approach is the use of targeted therapies, such as anti-angiogenic drugs, that aim to inhibit the formation of new blood vessels in the AVM.
Navigating Recovery and Rehabilitation after Arteriovenous Malformation Surgery
Recovery and rehabilitation play a crucial role in the overall outcome of Arteriovenous Malformation surgery. The road to recovery may vary depending on the individual and the extent of the surgery.
The Road to Post-Surgery Healing
After Arteriovenous Malformation surgery, it is important to follow the post-operative care instructions provided by the healthcare team. This may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments for regular check-ups.
Physical and Occupational Therapy for Arteriovenous Malformation Patients
Physical and occupational therapy can greatly assist in the recovery and rehabilitation process for Arteriovenous Malformation patients. These therapies focus on improving strength, mobility, and functional abilities to enhance overall quality of life.
Psychological Support for Arteriovenous Malformation Survivors
Living with Arteriovenous Malformation can be emotionally challenging. It is essential for survivors to have access to psychological support to cope with anxiety, depression, and other psychological symptoms that may arise as a result of the condition or the surgery.
FAQ
Question: What is Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain or spinal cord. Unlike normal blood vessels, which form a network of arteries that branch out into capillaries and then join together to form veins, AVMs have direct connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This disrupts the normal blood flow and can lead to serious health issues.
Question: What are the causes of Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: The exact cause of Arteriovenous Malformation is still not fully understood. It is believed to be a congenital condition, meaning it develops during fetal development. Genetic factors may also play a role in the development of AVM. However, in most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Question: What are the symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: The symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation can vary depending on the location and size of the malformation. Some common symptoms include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in the limbs, difficulty speaking or understanding language, vision problems, and balance and coordination issues.
Question: What diagnostic tools are used for Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: Diagnostic tools for Arteriovenous Malformation include Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT) scans, Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA), Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA), and Transcranial Doppler (TCD) Ultrasound.
Question: What are the treatment options for Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: The treatment approach for Arteriovenous Malformation depends on several factors such as the size, location, and symptoms associated with the malformation. Invasive treatment approaches involve surgical interventions to remove or occlude the AVM, such as microsurgical resection and endovascular embolization. Non-invasive options include radiosurgery using focused radiation to shrink the malformation.
Question: What are some novel surgical techniques for AVM treatment?
Answer: Advancements in surgical techniques have greatly improved the success rates and outcomes of AVM treatment. One such technique is intraoperative angiography, which allows real-time imaging during the surgery to confirm the complete removal or occlusion of the AVM.
Question: What is involved in recovery and rehabilitation after AVM surgery?
Answer: Recovery and rehabilitation after AVM surgery may involve following post-operative care instructions, physical and occupational therapy to improve strength and functional abilities, and accessing psychological support to cope with emotional challenges.
Question: Are there emerging therapies for the treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation?
Answer: Researchers are constantly exploring new therapies for the treatment of Arteriovenous Malformation. One promising approach is the use of targeted therapies, such as anti-angiogenic drugs, that aim to inhibit the formation of new blood vessels in the AVM.